Rapid Prototyping in 3D Printing: Definitions, Types, and Methods.
To meet the growing needs of customers, product developers are actively seeking ways to optimize manufacturing processes, especially in terms of cost control and production efficiency. This has led to an urgent demand for rapid prototyping technologies. Rapid prototyping, with a focus on machinery (especially 3D printers), tightly integrates computer technology with the design and manufacture of actual parts. It encompasses a range of techniques precisely controlled by computers.
In the realm of 3D printing for rapid prototyping, various technologies are involved, including additive manufacturing, subtractive manufacturing, and casting. Among these, 3D printing plays a crucial role and includes techniques such as Stereolithography (SLA), Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Powder Bed Fusion, and Selective Laser Melting (SLM). This article will delve deeply into the rapid prototyping techniques of 3D printing, exploring their types, methods of application, and compare them with traditional tools to highlight their unique advantages and value.
♦What is Rapid Prototyping in 3D Printing?◊
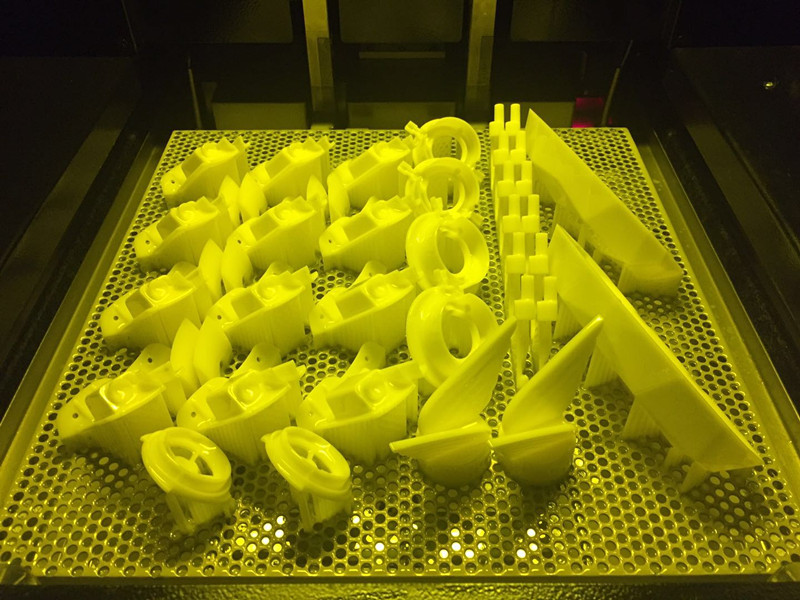
Rapid prototyping in 3D printing refers to the process of using advanced 3D printing technology to quickly realize the design and manufacture of physical models. This technique is not only fast, facilitating rapid market delivery, but it also employs an additive manufacturing approach. The physical parts produced through this method are known as high-fidelity prototypes, which nearly match the final products in both appearance and performance. Although technologies like casting and CNC machining are also involved in rapid prototyping, 3D printing is particularly favored in the concept verification stage due to its unique advantages. It’s important to note that prototyping is not an end in itself but a means to achieve final design objectives. Through continuous iteration and optimization of prototypes, the mass production of fully designed parts is eventually facilitated. Below is a typical example of the rapid prototyping process using 3D printing by ACMEMFG:What are the advantages and disadvantages of rapid prototyping?The advantages of rapid prototyping are its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. It can quickly realize the production of physical parts, allowing designers to feel in advance how the final product will look and operate, so that necessary improvements and optimizations can be made before final production. However, rapid prototyping also has some disadvantages. Sometimes, product developers may focus too much on a limited prototype and neglect a thorough analysis of the product, which may affect the quality of the final product. But it is worth mentioning that the process is highly automated, reducing labor costs.What is rapid prototyping used for?Rapid prototyping plays an important role in several fields. It can be used both for the production of physical models and for the verification of digital models. This process is fast and efficient, helping to identify and resolve potential issues before the final iteration, thereby improving the quality of the product.
♦What is Rapid Prototyping?◊
As for the methods of rapid prototyping, they encompass a variety of technologies, including 3D printing (additive manufacturing), high-speed machining (subtractive manufacturing), injection molding, and casting. Each method has its unique features, and the appropriate technology can be chosen based on specific needs.
How Does Rapid Prototyping Work?
The working principle of rapid prototyping is relatively straightforward. First, a digital 3D model of the part is generated using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software and converted into a specific file format. Then, slicing software is used to divide the 3D model into a series of 2D layered slices. Next, the 3D printer builds the part layer by layer based on this slice information until the entire object is completed. During the printing process, support structures may need to be added to prevent the part from warping or deforming. Finally, the prototype undergoes necessary post-processing, such as sanding, cleaning, and painting, to achieve the desired surface finish.
How to Use Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototype design is aimed at reducing the production cost of new products and shortening delivery times. Before the physical model is validated, the prototype first exists in conceptual form, guiding the team towards the next steps in the iterative process. To ensure the efficiency of the rapid prototyping process, consider the following points:
Initial prototypes are often relatively rough and may be made using different materials and colors. Once the basic form of the prototype is determined, the next step is post-processing, aimed at enhancing product quality to meet requirements.
Subsequently, the prototype gradually transitions to a functional prototype, although it may not yet fully realize all functions. At this stage, prototypes are usually made using the same materials as the final product and undergo performance evaluations to ensure they match the expected results. Evaluations may involve the prototype's adaptability to specific conditions, the fit of assembly points, and other aspects.
Why Do Engineers Favor Rapid Prototyping?
Engineers opt for rapid prototyping technology because it allows for the fast development of prototype models directly from CAD files. This means engineers can modify designs based on actual test feedback, rather than just relying on conceptual frameworks. Before mass production, they can visually assess the final or actual product's appearance and performance, enabling them to make more informed decisions.
♦Is Rapid Prototyping the Same as 3D Printing?◊
No, rapid prototyping and 3D printing are technically different. Although these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they do not represent the exact same concepts. Rapid prototyping is a broader term that refers to the process of quickly developing and creating product prototypes using computer-aided software. 3D printing, on the other hand, is one of the specific technological means to achieve this process, responsible for building three-dimensional physical models from CAD models. Therefore, 3D printing is just one method employed in rapid prototyping.
How Does Rapid Prototyping Differ from Traditional Machining?
Rapid prototyping and traditional machining differ in several significant ways. Firstly, rapid prototyping is an automated process that allows designers to quickly create product models via computer-aided software, whereas traditional machining relies more on manual operation and manual control. Secondly, the scope of rapid prototyping is relatively narrow, focusing primarily on the quick generation and validation of models. Traditional machining, however, encompasses a broader range of machining tools and processes such as lathes, drills, and milling machines, suitable for a wider range of manufacturing needs. Therefore, rapid prototyping typically offers superior speed and efficiency, while traditional machining excels in machining complexity and precision.♦Industrial-grade SLA 3D printers play a crucial role in rapid prototyping and offer many advantages, including:◊
Fast Production Speed: 3D printing technology can rapidly produce physical prototypes, typically within a few hours. This saves a significant amount of time compared to traditional prototyping methods such as casting or CNC machining.
Flexibility and Customization: 3D printing technology allows for quick customization of prototypes according to design requirements, without the need for additional tools or equipment changes. This flexibility makes it possible to rapidly verify and modify concepts during the design process.
Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to traditional manufacturing methods, 3D printing usually has lower costs, especially for small batch production or customized prototype production. This reduces the cost of prototype development, enabling more projects to be feasible.
Manufacturing of Complex Geometries: 3D printing can create complex geometric shapes and internal structures that are difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This allows designers to realize more complex and innovative designs.
Reduction of Material Waste: 3D printing is an additive manufacturing method that only uses the necessary materials to build an object, reducing material waste. This is particularly important for prototyping, as it can save costs and enhance sustainability.
Rapid Concept Validation: Due to the quick manufacturing speed of 3D printing, designers can rapidly produce multiple versions of prototypes and perform concept validation in a short period. This helps to accelerate the product development cycle and identify design issues early on.ACMEMFG is a company specializing in the manufacture of industrial-grade photopolymerization 3D printing equipment, headquartered in Yueyang, Hunan Province, China. Founded in 2018, the company focuses on photopolymerization 3D printing technology, and is committed to research and development, manufacturing, sales, and providing comprehensive application solutions.The founder, Mr. Zhang Zemin, is a seasoned researcher in the field, with extensive experience and deep technical expertise in the 3D printing industry. The company's product line includes LCD, DLP, and SLA series 3D printers, as well as various types of scanners for desktop and industrial uses, and photopolymer resins. These products are widely used in multiple sectors including automotive, electronics, handicrafts, medical, and education.
2024-04-17
Industry information
view details